Deploy the API using Flux
From the Flux documentation:
Flux is a tool for keeping Kubernetes clusters in sync with sources of configuration (like Git repositories), and automating updates to configuration when there is new code to deploy.
We are going to achieve the following:
- Each time we update the Helm chart it gets automatically deployed
- Each time a new image is updated it gets automatically deployed
To do that we need:
- Install the Flux CLI
- Bootstrap Flux in our local k8s cluster
- Configure a Flux Helm Repository
- Configure a Flux Helm Release
- Configure Flux image repository and automation policy
Uninstall Helm release
As Flux will be managing the Helm releases, we need to remove the Helm release create in the last section.
Use the following command:
helm uninstall learning-go-api --namespace learning-go-api
Install Flux CLI
The Flux CLI can be installed following the official documentation.
⚠ Don't follow any other step besides the installation of the CLI.
Bootstrap Flux in our local k8s cluster
To bootstrap Flux you need to export your GitHub personal token as an environment variable:
export GITHUB_TOKEN=<your-token>
Next, in the learning-go-api-iac local repository, create a folder to store
the Flux configurations:
mkdir flux
Run the bootstrap for the learning-go-api-iac on your personal GitHub account:
flux bootstrap github \
--owner=renato0307 \
--repository=learning-go-api-iac \
--personal \
--path=./flux \
--read-write-key \
--components-extra=image-reflector-controller,image-automation-controller
I want to highlight some of the actions executed by this command:
- Creates a list of k8s resources
- The definitions of those resources are added to the repository indicated in
the bootstrap command, in the path indicated by
--path - Adds an SSH deploy key to the repository, with read-write permissions
After the command executes successfully you should see in the terminal something like:
(...)
◎ waiting for Kustomization "flux-system/flux-system" to be reconciled
✔ Kustomization reconciled successfully
► confirming components are healthy
✔ helm-controller: deployment ready
✔ image-automation-controller: deployment ready
✔ image-reflector-controller: deployment ready
✔ kustomize-controller: deployment ready
✔ notification-controller: deployment ready
✔ source-controller: deployment ready
✔ all components are healthy
Next if you execute a git pull, the config files used to deploy Flux are
updated locally:
remote: Enumerating objects: 25, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (25/25), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (16/16), done.
remote: Total 21 (delta 8), reused 13 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (21/21), 27.05 KiB | 814.00 KiB/s, done.
From github.com:renato0307/learning-go-api-iac
b75329f..d35647b main -> origin/main
Updating b75329f..d35647b
Fast-forward
clusters/local-kind/release.yaml | 4 +-
flux/flux-system/gotk-components.yaml | 6403 ++++++++
flux/flux-system/gotk-sync.yaml | 27 +
flux/flux-system/kustomization.yaml | 5 +
4 files changed, 6437 insertions(+), 2 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 flux/flux-system/gotk-components.yaml
create mode 100644 flux/flux-system/gotk-sync.yaml
create mode 100644 flux/flux-system/kustomization.yaml
If you want to understand what components are created, feel free to take a look into those files.
As an alternative you can run a kubectl get all in the flux-system
namespace:
kubectl -n flux-system get all
The result should be similar to:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/helm-controller-779b58df6b-ppjgs 1/1 Running 0 7m39s
pod/image-automation-controller-787b4cf8b7-ts9r9 1/1 Running 0 7m39s
pod/image-reflector-controller-6d94666b7d-2ttt2 1/1 Running 0 7m39s
pod/kustomize-controller-5db6bfc56d-k7kpc 1/1 Running 0 7m39s
pod/notification-controller-7ccfbfbb98-pmlgf 1/1 Running 0 7m39s
pod/source-controller-565f8fbbff-lnw4m 1/1 Running 0 7m39s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/notification-controller ClusterIP 10.96.228.107 <none> 80/TCP 7m39s
service/source-controller ClusterIP 10.96.181.190 <none> 80/TCP 7m39s
service/webhook-receiver ClusterIP 10.96.154.81 <none> 80/TCP 7m39s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/helm-controller 1/1 1 1 7m39s
deployment.apps/image-automation-controller 1/1 1 1 7m39s
deployment.apps/image-reflector-controller 1/1 1 1 7m39s
deployment.apps/kustomize-controller 1/1 1 1 7m39s
deployment.apps/notification-controller 1/1 1 1 7m39s
deployment.apps/source-controller 1/1 1 1 7m39s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/helm-controller-779b58df6b 1 1 1 7m39s
replicaset.apps/image-automation-controller-787b4cf8b7 1 1 1 7m39s
replicaset.apps/image-reflector-controller-6d94666b7d 1 1 1 7m39s
replicaset.apps/kustomize-controller-5db6bfc56d 1 1 1 7m39s
replicaset.apps/notification-controller-7ccfbfbb98 1 1 1 7m39s
replicaset.apps/source-controller-565f8fbbff 1 1 1 7m39s
Configure a Flux Helm Repository
The next step is to tell Flux where to fetch Helm charts.
Inside the flux folder create the helm-git-repository.yaml file:
touch flux/helm-git-repository.yaml
The contents of this file are:
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta1
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: learning-go-api-iac-repo
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 1m
url: https://github.com/renato0307/learning-go-api-iac
ref:
branch: main
ignore: |
# exclude all
/*
# include charts
directory
!/charts/
As you can see by the kind and apiVersion elements, this is a custom
resource type defined by Flux.
Configure a Flux Helm Release
The next step is to tell Flux which charts to install.
Inside the flux folder create the helm-release.yaml file:
touch flux/helm-release.yaml
The contents of this file are:
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: learning-go-api
namespace: learning-go-api
spec:
interval: 5m
chart:
spec:
interval: 1m
chart: ./charts/learning-go-api
version: '>=0.0.1 <1.0.0'
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: learning-go-api-iac-repo
namespace: flux-system
values:
image:
tag: 0.0.3 # {"$imagepolicy": "flux-system:learning-go-api:tag"}
replicaCount: 2
Let's take a look at the spec/chart element:
- It will check for new versions every minute
- The chart to install in located in
./charts/learning-go-api - It will update all charts with versions >=0.0.1 and <1.0.0
- It will fetch the charts from the repository defined before
In the spec/values element:
- It will override the image tag to be used in the Helm chart
- The comment on the
tagelement will be used later to update the image automatically (don't remove it) - It will override the number of pod replicas
Commit and push the files
As Flux is already monitoring this repository, if you commit and push these two files, Flux will apply them in the k8s cluster.
Let's do that:
git add .
git commit -m "add helm configurations to flux`
git push
After a couple of minutes if you get all resources from the learning-go-api
namespace you'll see the API deployed.
To get all resources execute:
kubectl -n learning-go-api get all
The result will be similar to:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/learning-go-api-7c8878597b-7snnm 1/1 Running 0 2m15s
pod/learning-go-api-7c8878597b-zbfxd 1/1 Running 0 2m15s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/learning-go-api LoadBalancer 10.96.153.36 172.19.255.200 9000:32741/TCP 2m15s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/learning-go-api 2/2 2 2 2m15s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/learning-go-api-7c8878597b 2 2 2 2m15s
Before we turn on the image automation, let's check the version being used by the pods:
kubectl -n learning-go-api describe deploy learning-go-api
The result should be:
Name: learning-go-api
Namespace: learning-go-api
CreationTimestamp: Thu, 30 Dec 2021 08:40:55 +0000
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/instance=learning-go-api
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=Helm
app.kubernetes.io/name=learning-go-api
app.kubernetes.io/version=0.0.3
helm.sh/chart=learning-go-api-0.1.0
helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/name=learning-go-api
helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/namespace=learning-go-api
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
meta.helm.sh/release-name: learning-go-api
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: learning-go-api
Selector: app.kubernetes.io/instance=learning-go-api,app.kubernetes.io/name=learning-go-api
Replicas: 2 desired | 2 updated | 2 total | 2 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/instance=learning-go-api
app.kubernetes.io/name=learning-go-api
Service Account: default
Containers:
learning-go-api:
Image: renato0307/learning-go-api:0.0.3
Port: 8080/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
(...)
As we can see, version 0.0.3 is in use.
Configure Flux image repository and automation policy
To make Flux update the images in the Helm chart we need to configure three resources:
- The image repository
- An image policy to define which images should we monitor to update
- An image update automation
This can be achieved by running the following commands.
The first one generates an ImageRepository resource which checks for images
in my personal Docker Hub repository:
flux create image repository learning-go-api \
--image=renato0307/learning-go-api \
--interval=1m \
--export > ./flux/image-repository.yaml
The second one generates an ImagePolicy resource so Flux checks for image
with versions >=0.0.1 and <1.0.0:
flux create image policy learning-go-api \
--image-ref=learning-go-api \
--select-semver='>=0.0.1 <1.0.0' \
--export > ./flux/image-policy.yaml
The last one generates an ImageUpdateAutomation resource which sets the
GitHub repository settings that allow to update the Helm releases.
flux create image update flux-system \
--git-repo-ref=flux-system \
--git-repo-path=./flux \
--checkout-branch=main \
--push-branch=main \
--author-name=fluxcdbot \
--author-email=fluxcdbot@users.noreply.github.com \
--commit-template="" \
--export > ./flux/image-update-automation.yaml
⚠ This will effectively change files in the GitHub repository.
After running all commands, feel free to inspect the content of the files.
Commit and push the files
As Flux is already monitoring this repository, if you commit and push these two files, Flux will apply them in the k8s cluster.
Let's do that:
git add .
git commit -m "add flux image update automation`
git push
After a couple of minutes we can check the image update resources.
For the image repositories run:
kubectl -n flux-system get imagerepositories.image.toolkit.fluxcd.io
The result should be similar to:
NAME LAST SCAN TAGS
learning-go-api 2021-12-30T09:07:33Z 3
For the image policies run:
kubectl -n flux-system get imagepolicies.image.toolkit.fluxcd.io
The result should be similar to:
NAME LATESTIMAGE
learning-go-api renato0307/learning-go-api:0.0.3
For the image update automation run:
kubectl -n flux-system get imageupdateautomations.image.toolkit.fluxcd.io
The result should be similar to:
NAME LAST RUN
flux-system 2021-12-30T07:09:41Z
Deploying a new image of the API
To deploy a new image of the API, we need to create a new tag.
Go to the learning-go-api repository and run:
git tag -a v0.0.4 -m "v0.0.4"
git push origin v0.0.4
Wait for a couple of minutes for the build image GitHub action to generate and publish the images in Docker Hub.
Running the following command:
kubectl -n flux-system get imagepolicies.image.toolkit.fluxcd.io
We can see Flux already detected the latest version of the image:
NAME LATESTIMAGE
learning-go-api renato0307/learning-go-api:0.0.4
If we list the pods:
kubectl -n learning-go-api get po
We will see some terminating and another ones with a very recent AGE
(if you don't see it, wait a couple more minutes):
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
learning-go-api-58c875f648-v9vzr 1/1 Running 0 17s
learning-go-api-58c875f648-wqbvt 1/1 Running 0 9s
learning-go-api-7c8878597b-7snnm 0/1 Terminating 0 37m
We can describe one of the pods:
kubectl -n learning-go-api describe po learning-go-api-58c875f648-v9vzr
And check the image version in use:
Image: renato0307/learning-go-api:0.0.4
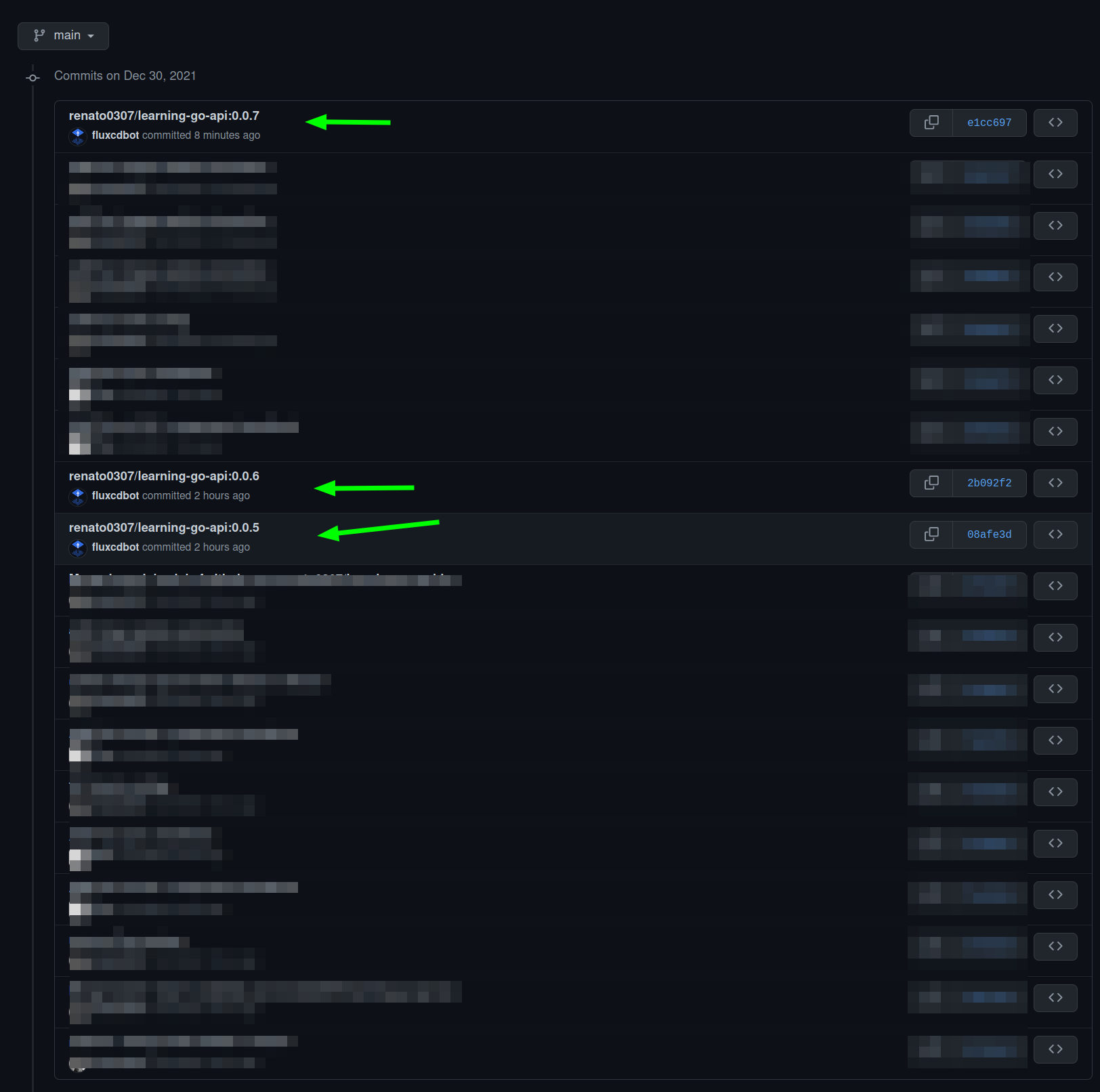
If you head to GitHub you'll be able to see the commits done by Flux, due to the image updates:
Wrap up
And that's it.
We are now able to deploy our API automatically just by creating new tags in GitHub.
Next
The next section is Change API file structure.