GitHub actions for the API
The GitHub actions for the API are going to be a little more complex than the ones we did for the Library.
In this case we want:
- To run the tests to ensure everything is OK, before each push or pull request
- Generate a new container image each time a new version of the API is created
Running tests action
This is going to be very similar to the one we did for the Library. You can just copy the same workflow file definition.
First create the workflows folder:
mkdir -p .github/workflows
Next create the .github/workflows/test.yaml file with the following contents:
name: Test
on:
push:
pull_request:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Go
uses: actions/setup-go@v2
with:
go-version: 1.17
- name: Test
run: go test -v ./...
This workflow will run tests recursively on any push or pull_request .
We can test this workflow using act.
To execute act simulating a push event run the following command:
act push
The first execution will take some time as the docker containers need to be downloaded but in the end you should see something like:
[Test/build] ⭐ Run Test
(...)
| PASS
| ok github.com/renato0307/learning-go-api/programming 0.006s
[Test/build] ✅ Success - Test
Finish up by committing and pushing the changes to GitHub.
After a couple of minutes, head to GitHub and check the result, like we did for the library.
Create container image action
Before anything else you need to create a DockerHub account and generate and access token.
Your Docker ID will be used in the same place you see renato0307 below
(this is my personal Docker ID).
This action/workflow needs to:
- Generate tags and metadata to be applied to the images
- Build images
- Upload images to a repository
Start by creating a new workflow definition:
touch .github/workflows/build-image.yml
The contents of this file is:
name: Build Docker Image
on: # Triggers the workflow when an image is pushed
push:
tags:
- 'v*.*.*'
jobs:
docker:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v2
# Generate tags and metadata to be applied to the images
- name: Docker meta
id: meta
uses: docker/metadata-action@v3
with:
# list of Docker images to use as base name for tags
images: renato0307/learning-go-api
# generate Docker tags based on the following events/attributes
tags: |
type=schedule
type=ref,event=branch
type=ref,event=pr
type=semver,pattern=
# Setups QEMU and Docker Buildx for multi-architecture image building
- name: Set up QEMU
uses: docker/setup-qemu-action@v1
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
# Logins into DockerHub, the image repository
- name: Login to DockerHub
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
username: $
password: $
# Builds images and pushes them to the repository
- name: Build and push
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
with:
platforms: linux/amd64,linux/arm64
push: $
tags: $
labels: $
I would like to highlight the following:
- This workflow will be triggered when new tag is created in the repository.
The goal is images to be uploaded images with the tag
renato0307/learning-go-api:GITHUB_TAG, for example if the GitHub tag isv0.0.1, the image will have therenato0307/learning-go-api:v0.0.1tag. - The image tag generation assumes the GitHub tags follow the semantic
versioning approach (e.g.
v0.0.1) - We will generate images for the
linux/amd64andlinux/arm64, using QEMU and Docker Buildx to achieve that purpose.
Like we did before we are going to test this workflow using act.
We will need extra steps to be able to do it.
As this workflow uses tags, we need to pass that information to act, using
the -e parameter, which allows specify to path to GitHub event JSON file.
First create the .github/workflows/push-tag.json file:
touch .github/workflows/push-tag.json
The file contents are:
{
"push": {
"ref": "refs/tags/v0.0.1"
}
}
This will allows us to simulate the push of the v0.0.1 tag.
This workflow requires three secrets to execute:
- GITHUB_TOKEN (check here how to create one)
- DOCKER_HUB_USERNAME (created before)
- DOCKER_HUB_TOKEN (created before)
Get those and execute the following command:
act push \
-e .github/workflows/push-tag.json \
-s GITHUB_TOKEN \
-s DOCKER_HUB_USERNAME \
-s DOCKER_HUB_TOKEN
act will prompt for the values of the secrets.
After a successful execution head to Docker Hub and you can see the images already uploaded, like illustrated below.
The learning-go-api images shows up in the image list:
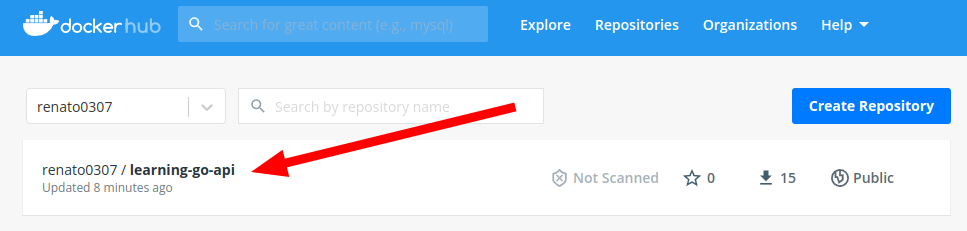
Can click to check the details:
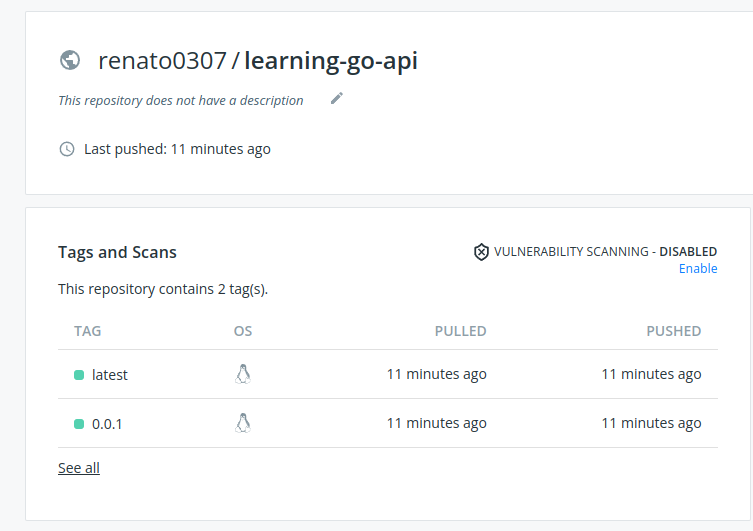
And by pressing the "See all" link we can see all tags and the architectures supported by the images:
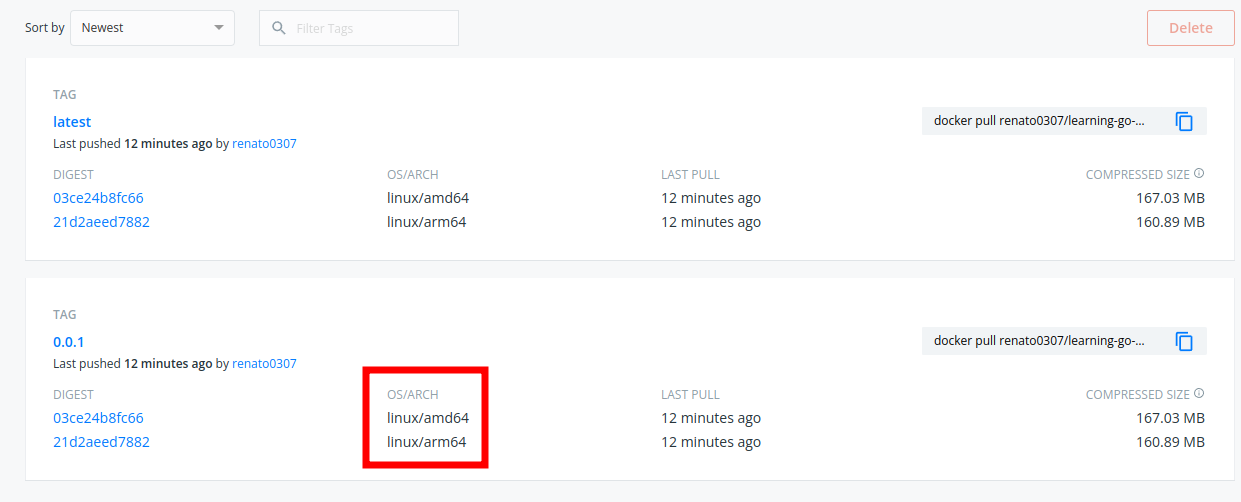
Once we have the workflow running locally, we need to make it work from GitHub.
For that we will need to create repository secrets.
Head to the repository Settings:
Go to the "Secrets" tab.
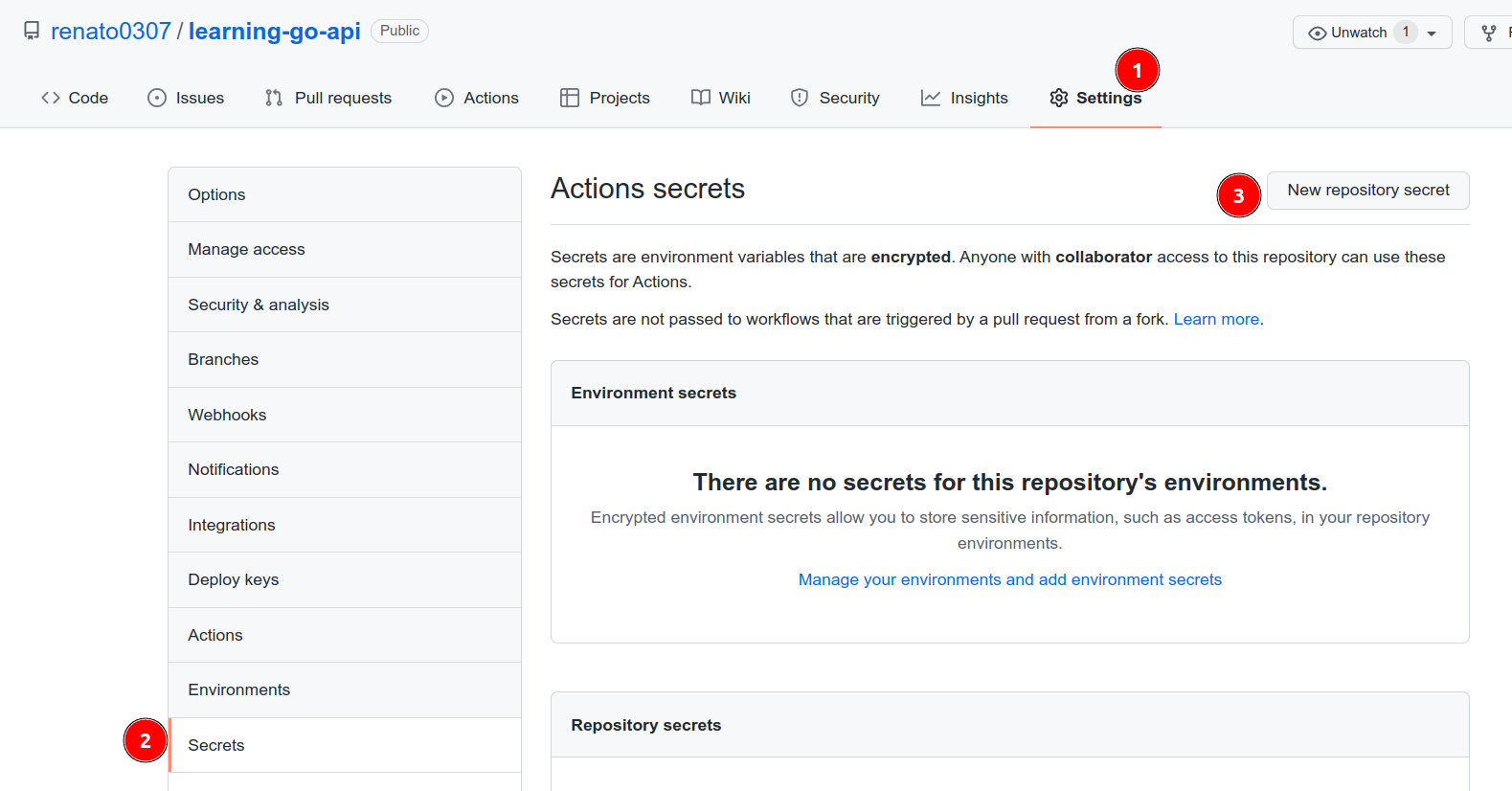
Add the DOCKER_HUB_USERNAME secret.
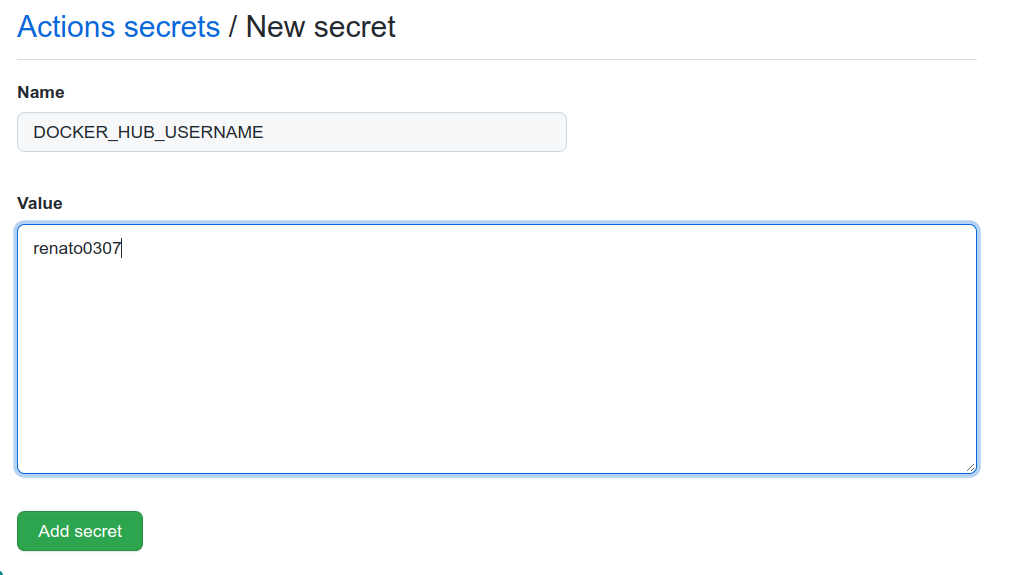
Add the DOCKER_HUB_TOKEN secret.
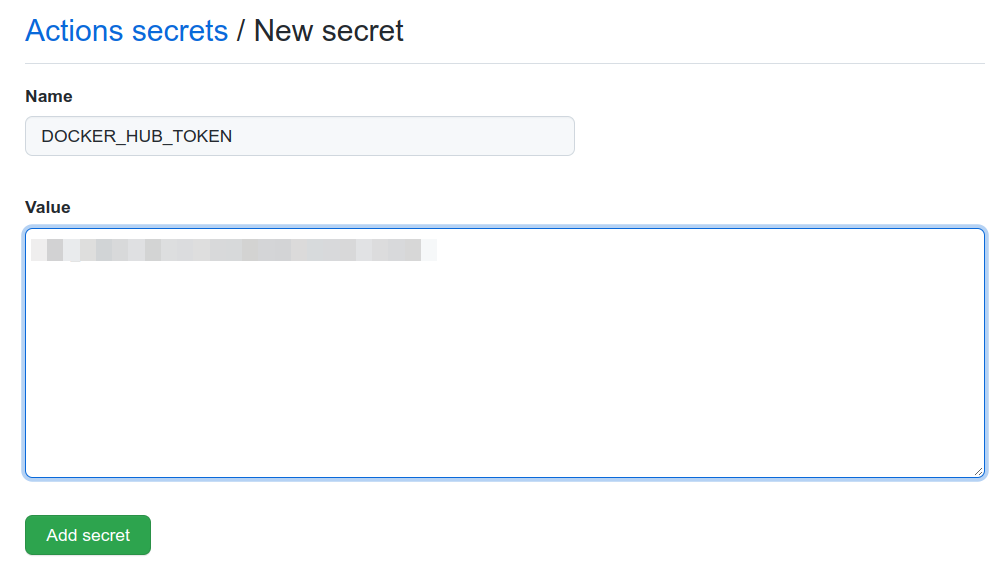
Check you have the two secrets in the list.
The GITHUB_TOKEN is not needed as GitHub makes it available by default.
After this, commit the changes and push the to GitHub.
To trigger the workflow in GitHub, create and push a new tag:
git tag -a v0.0.1 -m "v0.0.1"
git push origin v0.0.1
Go to the GitHub repository and the workflow will be running. Press the yellow dot to check the details:
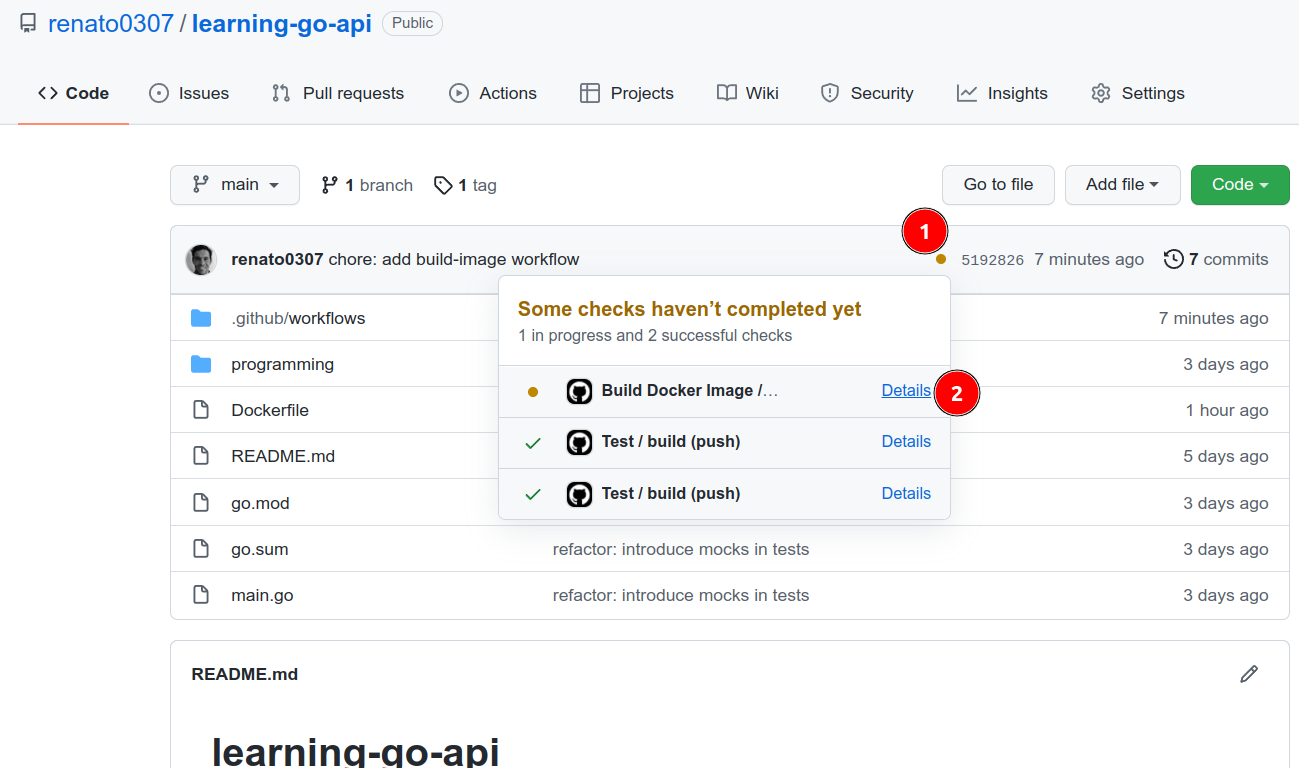
The workflow details:
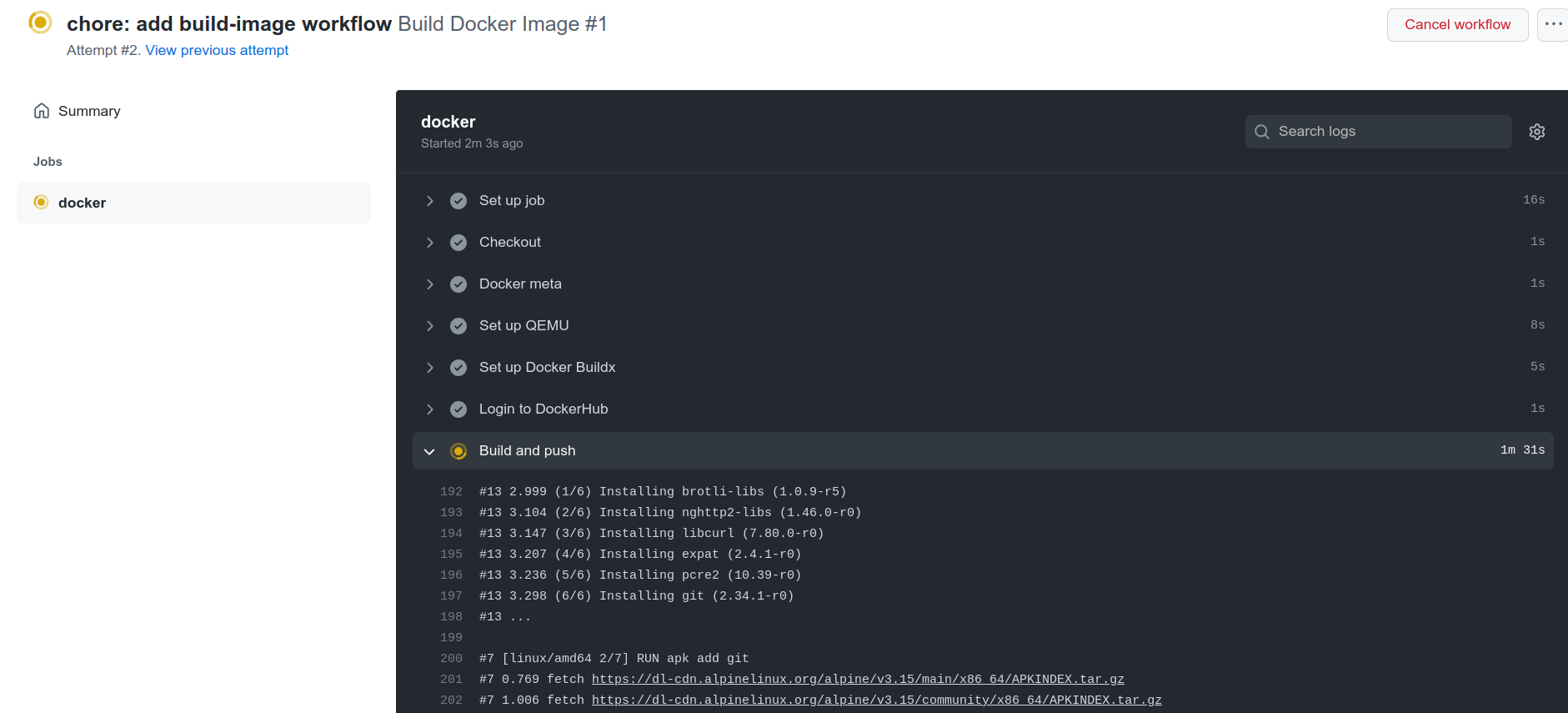
When the execution completes, go to Docker Hub and check the created/updated
image, like we did when testing using act.
Next
The next section is Add programming/jwtdebugger to the library and API.